What is moxibustion?
MOXIBUSTION, AKA “MOXA,” IS A SAFE AND WARMING TREATMENT THAT INVOLVES THE CONTROLLED BURNING OF A VERY SMALL AMOUNT OF DRIED MUGWORT DIRECTLY ON THE SKIN.
Moxa is used to treat a wide range of issues including:
pain, stiffness of the joints
decreased range of motion
ganglion cysts
digestive disorders
edema
menstrual disorders
urinary issues
jaw pain and tightness
herpes zoster
weakness and fatigue
and so much more!
I have had a lot of success in treating stubborn issues with moxa in my practice and, for many of my patients, it is one of their favorite parts of treatment. Personally, I find it to be a comforting experience and afterwards I feel the channels in my body more open and fluid, decreasing my sensations of pain and tightness.
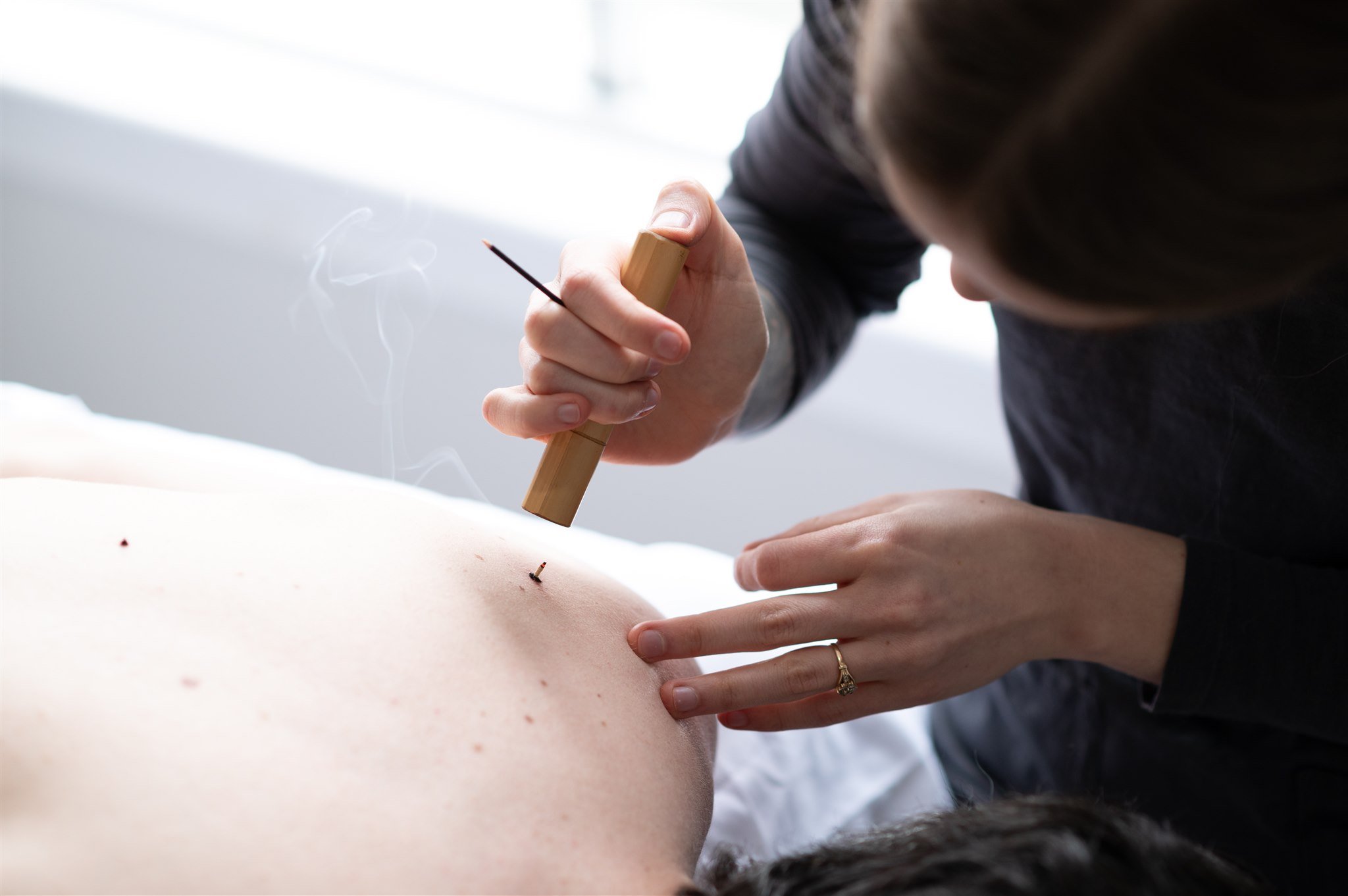
History of moxa
The art of moxibustion was being recorded in literature records dating as far back as the Warring States Period (475 B.C. to 221 B.C.). Since then, many doctors have written extensively on moxibustion being used to treat a vast array of diseases.
Since the mid-twentieth century, there has been an expansion in the treatment scope of moxibustion, thanks in part to the great progress in research on the subject.
Japan is largely to thank for this immense research on the mechanism behind moxibustion. In fact, many Japanese-style practitioners specialize in moxibustion exclusively.
How does it work?
Research has shown moxa to stimulate the shallow and deep tissues of the skin through thermal and radiation reactions. The effects of these reactions are many, including the enhanced metabolism of organs throughout the body, as well as stimulation of the immune system.
Mugwort leaves, and the smoke produced by burning them, have many therapeutic properties. Some of these properties include clearing free radicals and lipid peroxidation. The smoke of moxa also contains antiviral and antifungal components that disinfect air. The smoke has also been used to treat wounds and infections such as vaginal itching, uterine prolapse, anal fistulas, and warts.


